

NiftyWeb is a web service tool that provides an entry point to our cutting edge algorithms. NiftyWeb has a friendly interface and allows anyone to test or use our algorithms with minimal effort and with their optimal configurations. The website currently runs on a distributed network, where different nodes are responsible for specific algorithms.
STEPS is a multi-atlas segmentation propagation and fusion technique that generates probabilistic masks using a template library with associated manual segmentations (682 brain and 110 hippocampal manual segmentations). For the whole brain (hippocampus), the 30 (15) most similar deformed templates according to the NCC are fused into a consensus segmentation using the STEPS algorithm.
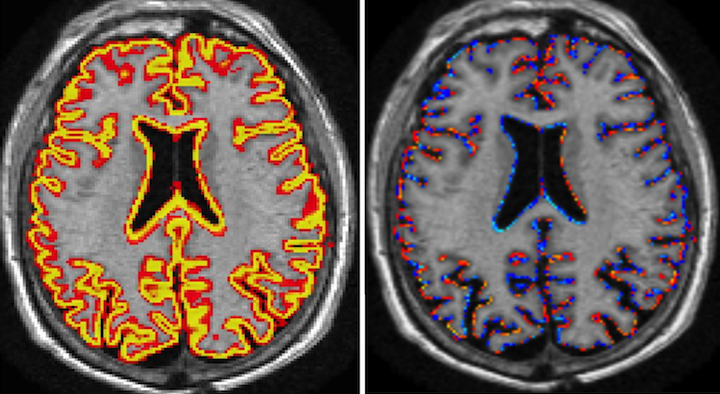
The generalised and extended formulation of the Boundary Shift Integral (GBSI) uses probabilistic segmentations in order to estimate anatomical changes between 2 time points. GBSI adaptively estimates a non-binary XOR region-of-interest from probabilistic brain segmentations of the baseline and repeat scans, in order to better localise and capture the brain atrophy.

The grey matter segmentation challenge will be held on the 13th of May immediately after the 2016 annual meeting of the ISMRM, in Singapore. The goal of the challenge is to test on a common dataset of anatomical magnetic resonance (MR) images of the healthy spinal cord algorithms for grey matter segmentation developed independently by different research groups across the world. The challenge aims to compare the performance of the different methods, with the aim of characterizing the state-of-the-art of the field as well as identifying opportunities for future improvement.
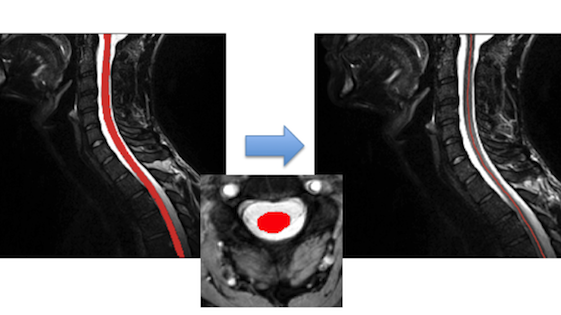
This is an automated tool based on the Spinal Cord Toolbox (SCT) for computing the cross-sectional area for each slice of a binarized segmentation of the spinal cord. The cross-sectional area is calculated by counting the pixels in each slice and then geometrically adjusting using centerline orientation.
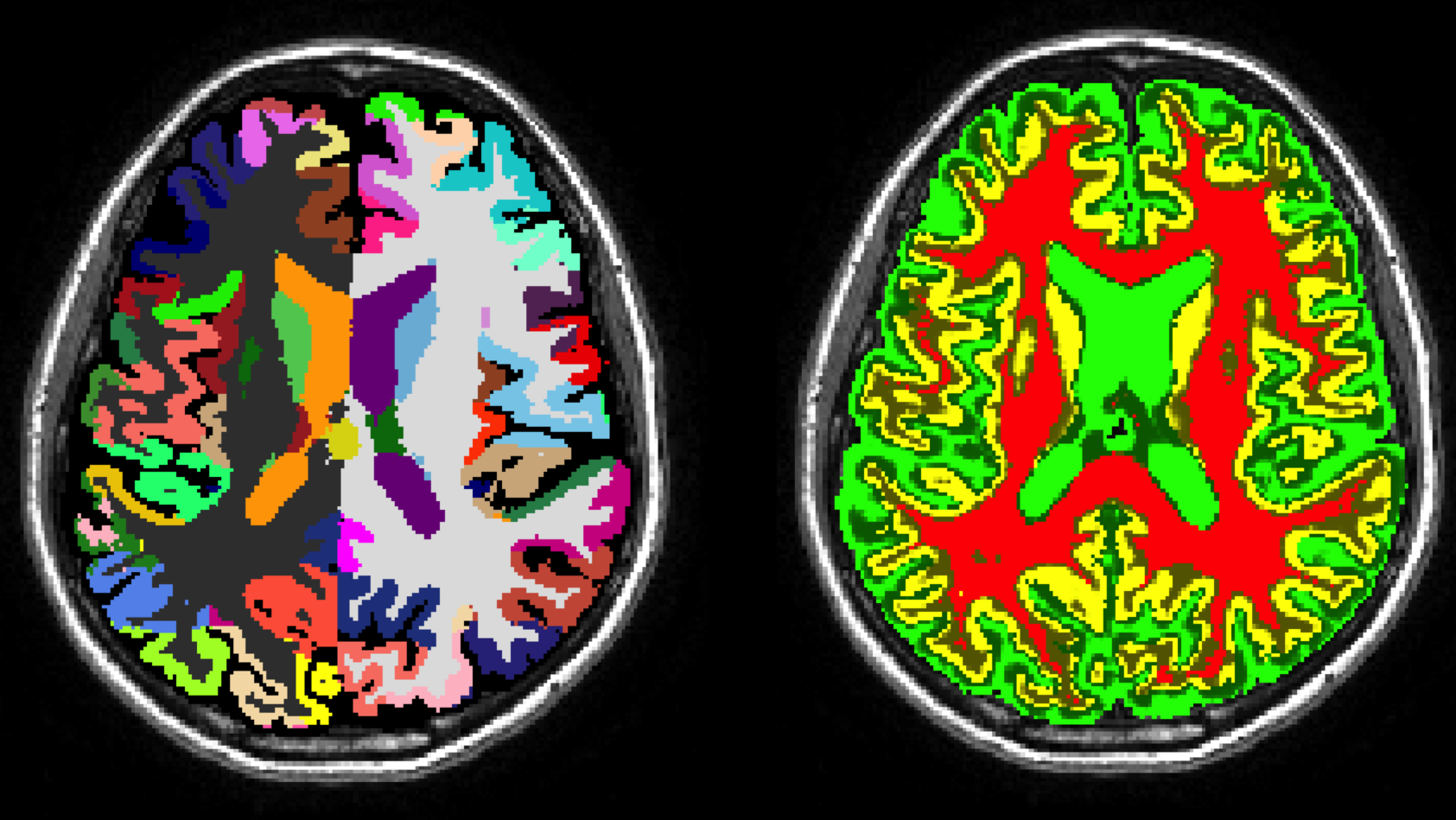
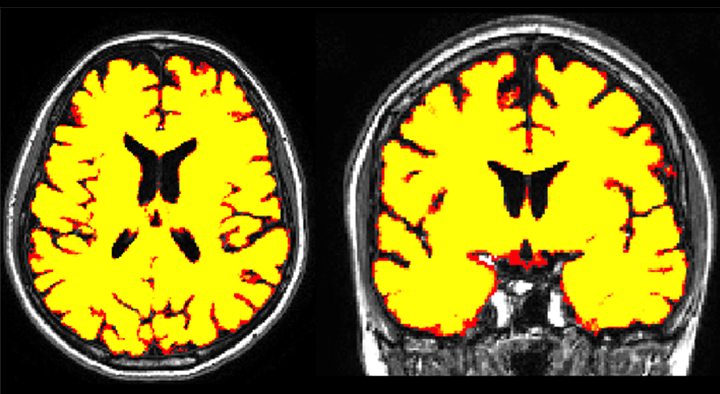
The GIF algorithm is an online brain extraction, tissue segmentation and parcelation tool for T1-weighted images. GIF, which stands for geodesical information flows, will be deployed as part of NiftySeg. You can download the parcelation labels in xml from here (v2, v3) and in excel from here (v2, v3).
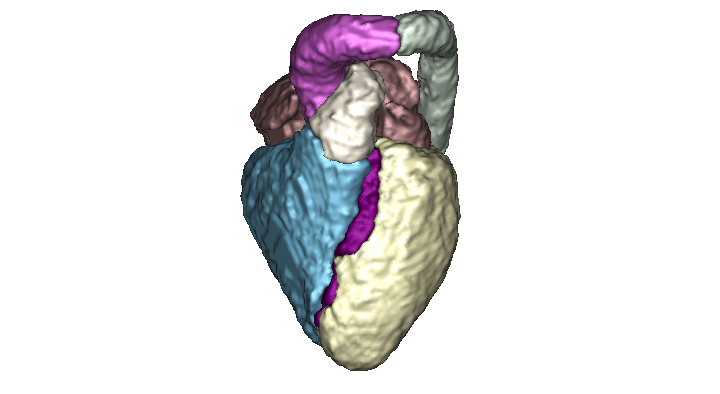
Fully automated method for the segmentation of the whole heart and the great vessels from 3D images. The method is based on a muti-atlas propagation segmentation scheme. Based on a cross correlation metric, our method selects the best atlases for propagation allowing the refinement of the segmentation at each iteration of the propagation.
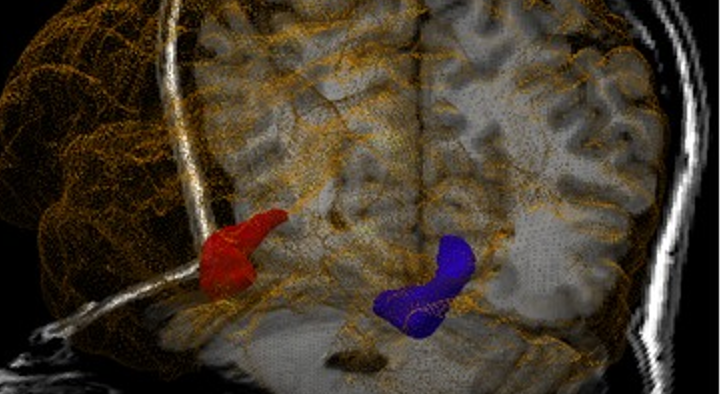
HIPPOSEG is an online tool for hippocampal and brain segmentation and morphometric characterisation, freely available to the clinical community. HIPPOSEG is based on STEPS, a multi-atlas segmentation propagation and fusion technique that automatically segments the hippocampi using a specific template library for epilepsy with 400 high-quality manual segmentations.
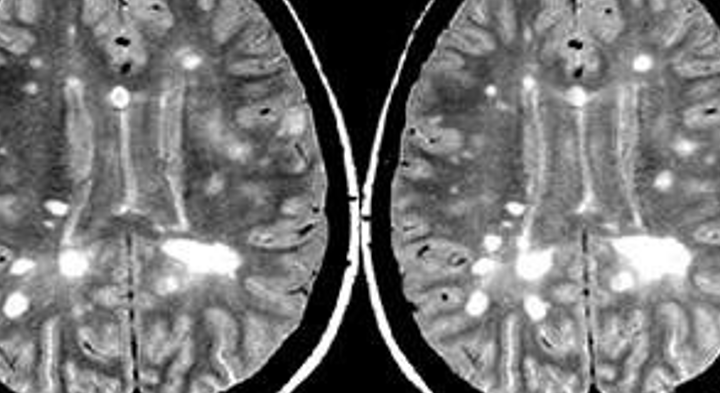
This pipeline uses the preprocessing steps from the boundary shift integral pipeline to detect new lesions, which are refined by a gradient boosting classifier. This version has been optimised for working with 3D FLAIR MR images. The baseline lesion segmentation needs to be provided and it can be computed using this tool.
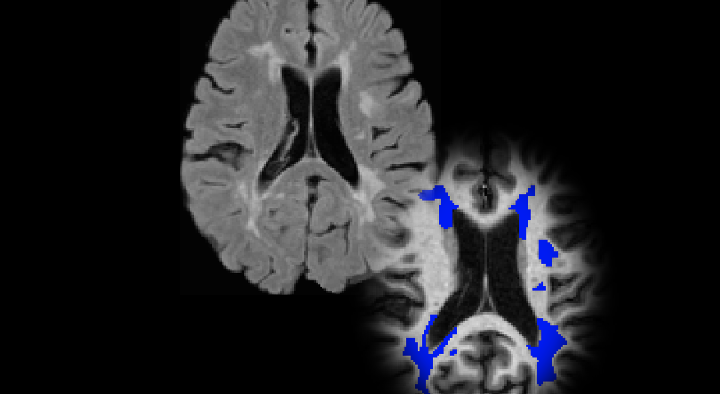
This is a modified version of nicMSLesions for MS lesion segmentation specifically trained with 46 manually segmented SPMS subjects from the Queen Square Multiple Sclerosis Centre at UCL. This version has been optimised for working with 3D FLAIR MR images. The code is available online at this GitHub repository.
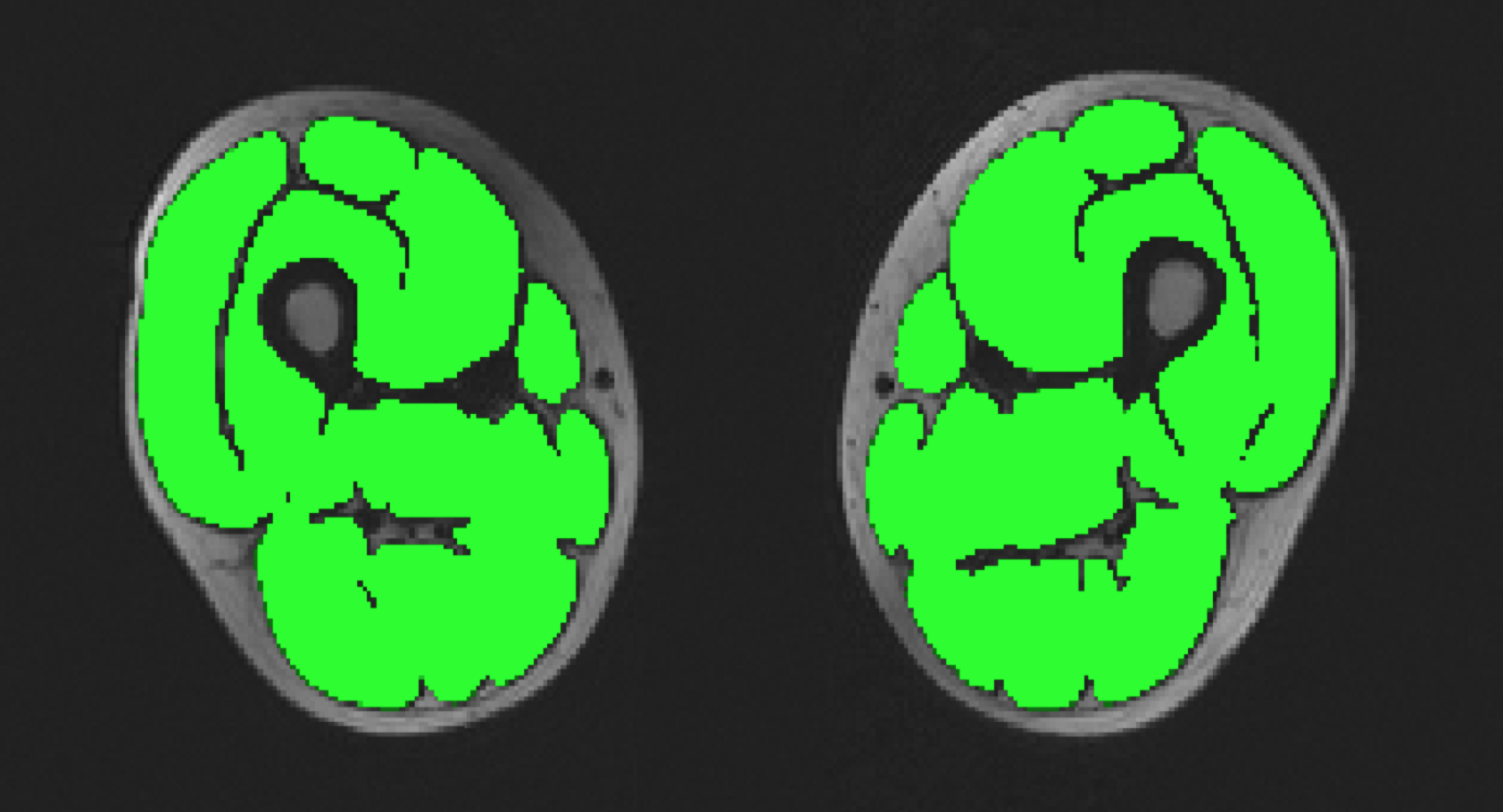
Musclesense is a trained artificial neural network for the anatomical segmentation of lower-limb MRI images in neuromuscular diseases. This simplified edition is tailored for lower-limb fat images obtained using generic MRI acquisition sequences, and methods of fat/water map extraction. A professional edition of Musclesense is available upon request for centres who are able to use our optimised 3-point Dixon sequence and the conventional algorithm of fat/water map extraction due to Glover and Schneider (1991).
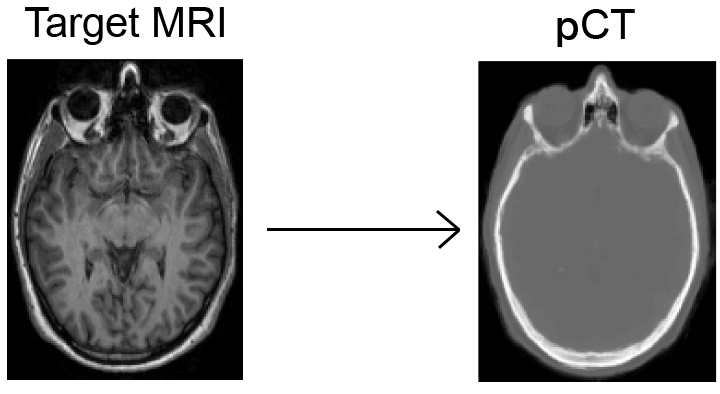
The "pseudo CT" synthesis tool is a fully automated software-as-service tool based on the work of Burgos et al. The aim of this tool is to generate CT-like images from aT1 or T2 image of a subject. It is implemented as an extension of the GIF algorithm. The implementation will be made available as part of NiftySeg.
The Quantitative Neuroradiology Initiative goal is to introduce automated quantitative MRI analysis into the clinical neuroradiology setting. We are aiming to develop an integrated platform for individual-patient quantitative reporting of disease-specific imaging biomarkers, to enhance both the clinical workflow and patient outcomes.
The MS Quantitative Neuroradiology Initiative automated report (QReport) can assist with the assessment of MRI in the setting of multiple sclerosis (MS) or suspected MS. Automated image segmentation techniques quantify lesion and brain volumes from a FLAIR MRI scan. The quantitative results are contextualised with healthy and MS reference data. The QReport has been developed for the cross-sectional analysis of a single patient's scan.